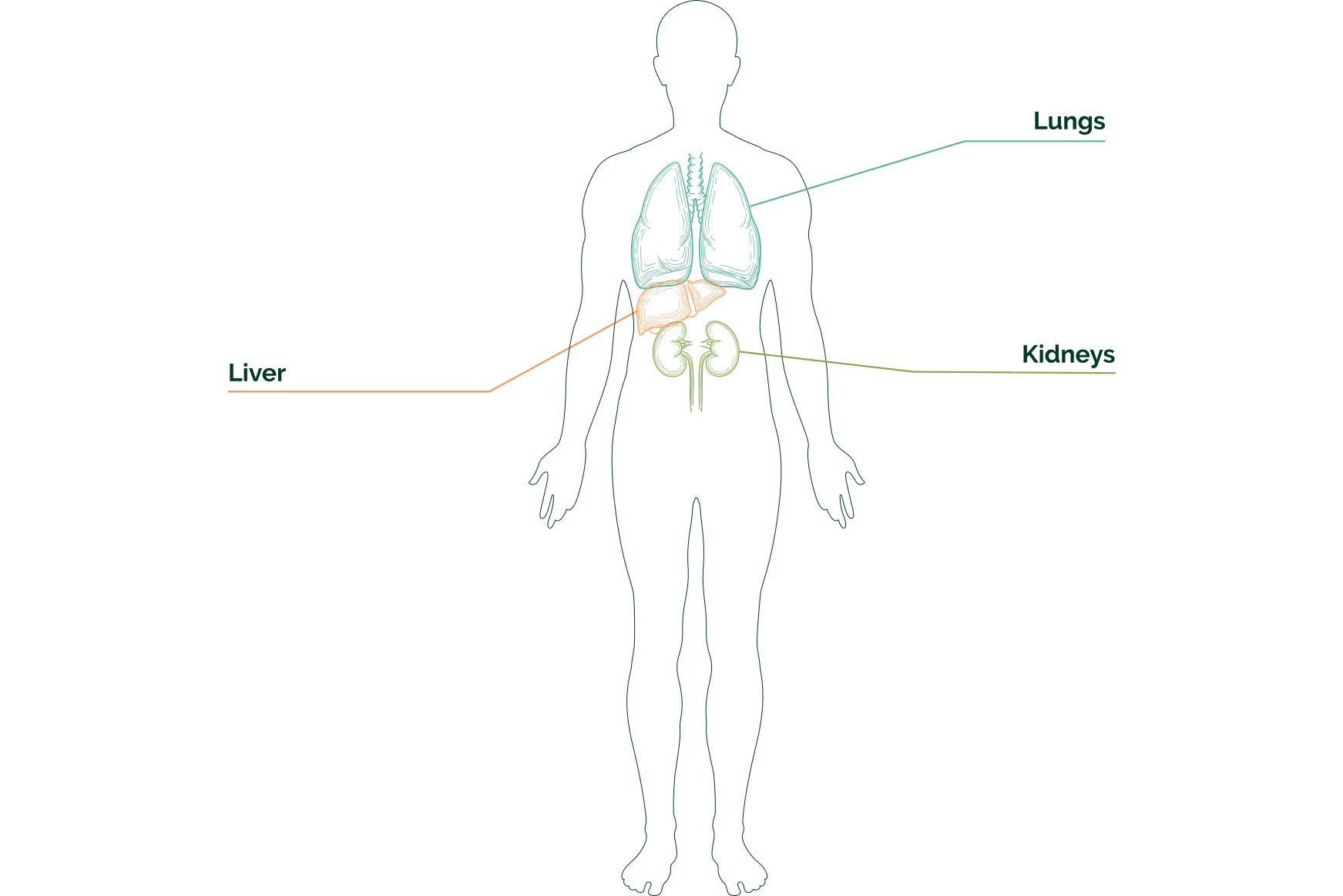
The Liver, Kidneys, and Lungs
Metabolic detoxification is a process by which the body eliminates toxins. The body has several mechanisms for eliminating toxins, including the liver, kidneys, and lungs.
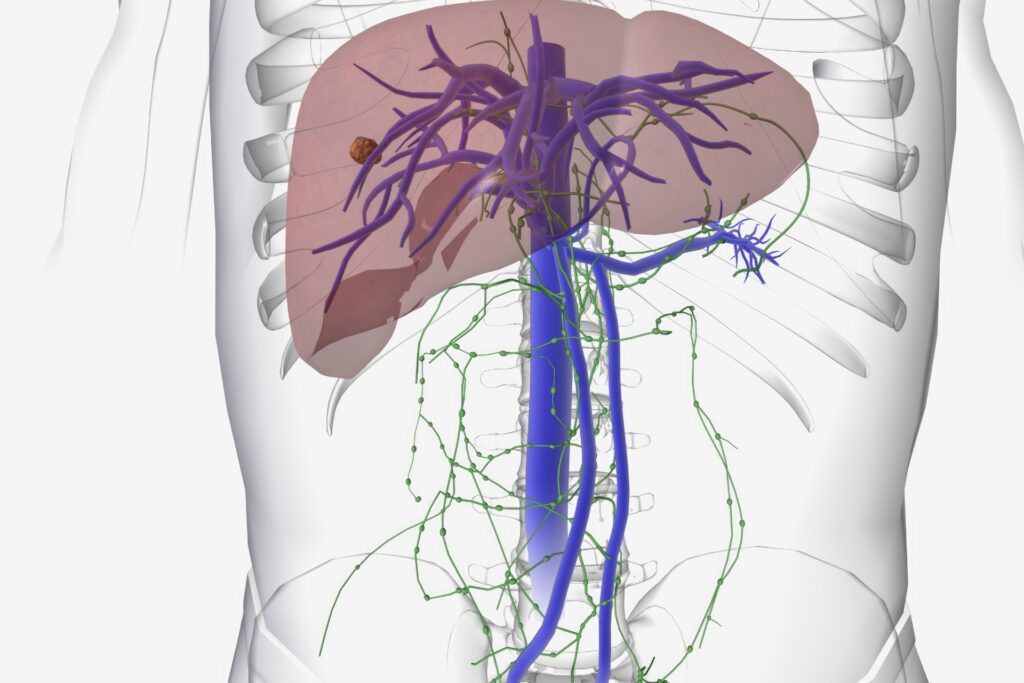
The liver is responsible for detoxifying many of the toxins that are introduced to the body. The kidneys are responsible for filtering toxins from the blood and excreting them in urine. The lungs are responsible for eliminating toxins from the body through exhalation.
Luckily, there is a way to help eliminate these toxins from your body and restore your health. We’ll discuss what metabolic toxins are and how you can get rid of them. But first, let’s define detoxification to better understand metabolic detoxification.
Detoxification is the physiological or medicinal removal of toxic substances from a living organism, including the human body, which is mainly carried out by the liver. It is both complementary (e.g., fasting), conventional (e.g., chelation or antitoxins), and those that are out of the realm of scientific plausibility (e.g., ionic foot detoxification).
 >
>
What is Metabolic Detoxification?
Metabolic detoxification is the pathway by which the body processes unwanted chemicals for elimination. The body metabolizes xenobiotics (foreign chemicals) and unnecessary endobiotics (endogenously produced chemicals) so they can be eliminated.
Excess hormones, environmental toxicants, and prescription drugs are all cleared via the same enzymatic detoxification systems. Metabolic detoxification is therefore essential for protecting the body from environmental factors and maintaining internal homeostasis. Pesticides, herbicides, food additives, plastics, heavy metals, and cigarette smoke are examples of toxicants that we may be exposed to in the environment.
The detox process can have side effects, depending on which substances are being eliminated and how quickly they are eliminated. Detoxification can cause fatigue, water retention, and headaches.
Some people may experience gastrointestinal (GI) problems such as diarrhea or constipation during or after detoxification.
Natural interventions, such as B vitamins and sulforaphane, may help support detoxification pathways by promoting the activity of essential enzymes.

Common Types of Toxins:
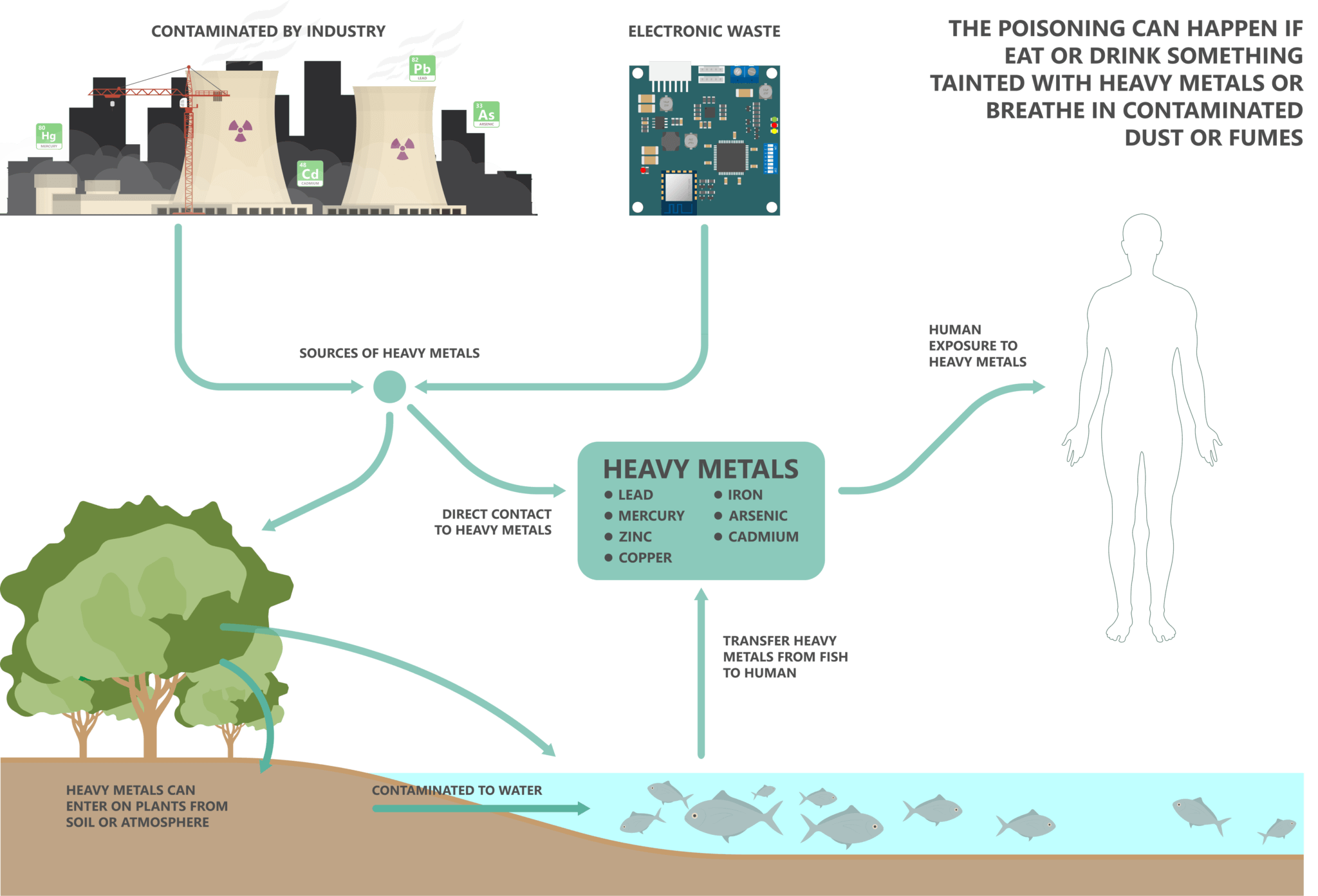
Toxins are substances that can harm our bodies and accumulate over time. Poor nutrition can increase the harmful effect of toxins which may be worsened by other factors, like heavy metals and pesticides.
External Toxins consist of:
- Air & water pollutants
- Cigarette smoke
- Certain personal care products
- Heavy metals
- Some household cleaning products
- Pesticides
- Preservatives & additives
What are the toxins found in food?
Some common foods or food ingredients are toxic. However, there are a few ingredients that may be harmful, particularly when consumed in large amounts.
- Refined vegetable and seed oils – consist of corn, sunflower, safflower, soybean, and cottonseed oils. These types of oils have been highly refined. They are also high in calories and fat.
- Bisphenol A and similar compounds – Bisphenol A (BPA) is a chemical compound that is typically found in plastics that hold many common foods and beverages, as well as inside metal food cans.
- Artificial trans fats – Artificial trans fats are made by pumping hydrogen into unsaturated oils such as soybean and corn oils to turn them into solid fats. In the past, they were commonly found in processed foods, such as margarine, snack foods, and packaged baked goods. However, trans fats are highly inflammatory, which contributes to heart disease.
- Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons – Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are considered environmental pollutants. As they can be created by burning organic materials, they can also be found in food.
- Coumarin in cinnamon – Coumarin is a toxic compound found in C. cassia, C. loureiroi, and C. burmannii cinnamon. When taken in high dosages, coumarin can cause cancer or liver damage.
- Added sugars – Added sugars are often referred to as “empty calories.” Sugar is high in fructose, and excess fructose intake has been linked to many serious conditions, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, fatty liver disease, and cancer. High sugar foods are often highly processed and include addictive properties, making it difficult for some people to regulate how much they eat.
- Mercury in fish – Fish is an excellent source of protein, but some deep sea fish can contain high levels of mercury, a known toxin. This is a result of the pollutant working its way up the food chain in the sea. These larger fish accumulate mercury in their bodies over time, which is eventually ingested by humans. Neurotoxins, such as mercury, can cause brain and nerve damage.
Who should think about doing a metabolic detox?
If you feel tired and achy all over your body, it might be time to consider a metabolic detox. The goal is to enhance the function and efficiency of your body’s cells, most especially the liver.
What indicators do you have that your body needs to detox?
- Anxiety
- General muscle and joint achiness
- Decreased concentration
- Headaches
- Unexplained Fatigue
- Poor gastrointestinal elimination/Constipation
- Blemishes and irritated skin
- Allergies
- Signs of poor immunity like repeated infections
- Puffy eyes
- Body Odor
- Acidity and bloating
- Insomnia
- Frequent mood swings
- Emotionally unstable, depressed, unmotivated, and lacking energy and enthusiasm for life
How long do metabolic detox symptoms last?
The duration of a metabolic detox is highly variable and depends on the individual. Some people may only experience symptoms for one day, while others may have symptoms that last up to two weeks. Symptoms usually begin to subside within the first week of detox. One of the most common metabolic detox symptoms is that your body will be feeling very sluggish.
The first step in metabolic detoxification is to limit the incoming exposure while supporting the liver’s ability to eliminate any chemicals that have built up over time.
Whenever possible, opt for organic produce, instead of those that are known to contain chemicals used in the farming process. This will support a healthy metabolic detoxification process.

The 3 Phases of Metabolic Detoxification
Phase 1—Enzymatic Transformation
Phase I occurs mostly in the liver and helps to transform dangerous, lipid-soluble molecules into less harmful intermediate products that will be easier to excrete. The bulk of the phase I transformation reactions are performed by a family of enzymes called the cytochrome P450s (CYPs). It is the first line of detoxification and must occur before phase II.
Phase 2—Enzymatic Conjugation
Phase 2 is the process of conjugation – the addition of a chemical group – to a by-product of phase I, making it water-soluble, and therefore less harmful. Once it is water-soluble, it can be excreted through the kidney and intestines through urine and bile.
Phase 3—Transport
Phase III refers to a highly concentrated anti-porter (transport) system of proteins in the body. It occurs post-phase II, where a chemical substance can undergo further metabolism and excretion. In the liver, phase III transporters move glutathione, sulfate, and glucuronide conjugates out of cells into the bile for elimination.
In the kidney and intestine, phase III transporters can remove xenobiotics from the blood for excretion from the body. This transport system ensures the movement of unwanted compounds out of the cell, and into detoxification organs.
What are the signs that your body is detoxing?
When you start to detox, you may experience symptoms like headaches, dizziness, or joint pain. All of these are normal and can be remedied by taking a turmeric supplement. Turmeric can relieve the symptoms of detoxification. A metabolic detox plan helps the body address and remove toxins.
Metabolic detoxification begins by limiting incoming exposure while at the same time supporting the liver’s ability to eliminate accumulated toxins. To know if your body is detoxing, you need to monitor your health and habits.
Metabolic detoxification may be performed at least once a year, sometimes twice a year.

How can you get rid of toxins in your body?
You can flush toxins from your body through a combination of detoxing and exercise.
Macronutrients, vitamins, minerals, and amino acids provide the body with the necessary building blocks to detoxify waste in the kidneys into urine or the liver into bile so that it can be excreted via the stools.
Tips on how you can detoxify your body
- Eat a wide range of organic vegetables to increase your fiber intake.
- Drink plenty of water, which supports the elimination of waste via the kidneys.
- Flush toxins from your body by drinking plenty of water and eating fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Get rid of heavy metals, chemicals, and other pollutants through proper waste disposal.
- Use detoxification programs that help to remove harmful substances from the body quickly.
Detox Your Body for Better Health
Metabolic detoxification is a process that helps rid the body of toxins. Anyone can benefit from it, but it is especially important for those with chronic health conditions.
The symptoms of metabolic detoxification can last anywhere from a few days to a few weeks, depending on the person’s unique situation. There are three phases of metabolic detoxification, and each one has its own set of benefits.
While there are many ways to rid the body of toxins, some methods are more effective than others. If you’re interested in undergoing metabolic detoxification, Contact us today.